What Is Swap In Forex
What is a Strange Substitution Swap?
A foreign commutation swap (also known as an FX bandy) is an understanding to simultaneously borrow ane currency and lend another at an initial date, so exchanging the amounts at maturity. It is useful for risk-gratuitous lending, every bit the swapped amounts are used as collateral for repayment.

Summary
- A foreign exchange swap refers to an agreement to simultaneously borrow one currency and lend another currency at an initial engagement, so exchanging the amounts at maturity.
- Leg ane is the transaction at the prevailing spot rate. Leg 2 is the transaction at the predetermined forrard rate.
- Short-dated foreign exchange swaps include overnight, tom-next, spot-next and spot-calendar week
- Foreign exchange swaps and cross currency swaps differ in involvement payments.
Understanding Foreign Substitution Swaps
For a foreign substitution swap to work, both parties must own a currency and need the currency that the counterparty owns. At that place are two "legs":
Leg 1 at the Initial Engagement
The first leg is a transaction at the prevailing spot rate. The parties swap amounts of the aforementioned value in their corresponding currencies at the spot rate. The spot rate is the exchange rate at the initial date.
Leg 2 at Maturity
The second leg is a transaction at the predetermined forward rate at maturity. The parties swap amounts again, so that each party receives the currency they loaned and returns the currency they borrowed.
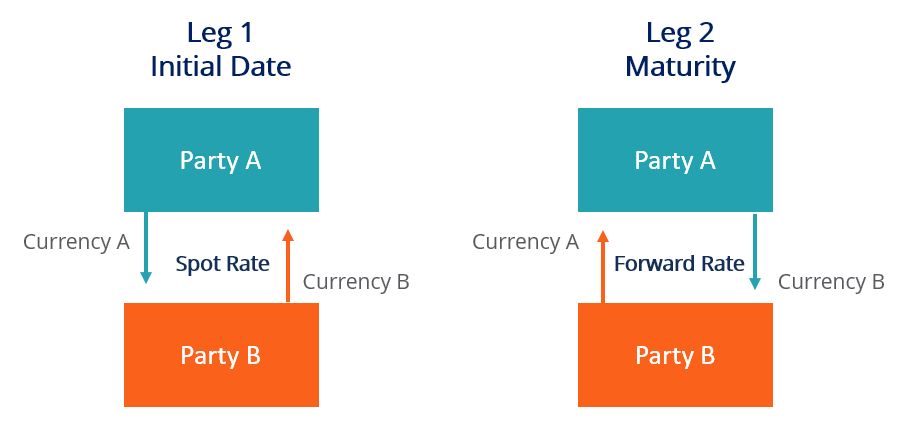
The frontward rate is the exchange rate on a future transaction, adamant between the parties, and is usually based on the expectations of the relative appreciation/depreciation of the currencies. Expectations stem from the interest rates offered by the currencies, as demonstrated in the interest rate parity. If currency A offers a higher interest charge per unit, it is to compensate for expected depreciation against currency B and vice versa.

Foreign substitution swaps are useful for borrowing/lending amounts without taking out a cross-border loan . It also eliminates foreign commutation risk by locking in the forrard charge per unit, making the hereafter payment known.
Applied Example
Party A is Canadian and needs EUR. Party B is European and needs CAD. The parties enter into a foreign commutation swap today with a maturity of six months. They agree to swap 1,000,000 EUR, or equivalently ane,500,000 CAD at the spot rate of 1.five EUR/CAD. They also agree on a frontwards charge per unit of 1.6 EUR/CAD because they expect the Canadian Dollar to depreciate relative to the Euro.
Today, Party A receives 1,000,000 Euros and gives 1,500,000 Canadian Dollars to Party B. In 6 months' time, Political party A returns 1,000,000 EUR and receives (1,000,000 EUR * one.6 EUR/CAD = one,600,000 CAD) from Party B, ending the strange commutation swap.
Short-Dated Foreign Exchange Swap
Brusk-dated foreign exchange swaps refer to those with a maturity of upward to i month. The FX market uses unlike shorthands for short-dated FX swaps, including:
- Overnight (O/N) – A swap today against tomorrow
- Tom-Next (T/North) – A swap tomorrow against the next day
- Spot-Next (S/N) – A bandy starting spot (T+2) against the next twenty-four hours
- Spot-Calendar week (S/W) – A bandy starting spot confronting a week after
Foreign Exchange Swap vs. Cantankerous Currency Bandy
Foreign exchange swaps and cross currency swaps are very like and are oftentimes mistaken as synonyms.
The major deviation between the two is interest payments. In a cross currency swap, both parties must pay periodic involvement payments in the currency they are borrowing. Unlike a foreign exchange swap where the parties own the corporeality they are swapping, cross currency swap parties are lending the amount from their domestic depository financial institution so swapping the loans.
Therefore, while foreign commutation swaps are riskless because the swapped amount acts every bit collateral for repayment, cross currency swaps are slightly riskier. There is default risk in the result the counterparty does not meet the involvement payments or lump sum payment at maturity, meaning the political party cannot pay their loan.
Learn More than
Thank y'all for reading CFI'southward guide on Foreign Substitution Swap. To keep learning and advance your career, the post-obit resource volition exist helpful:
- Currency Take chances
- Fixed vs. Pegged Exchange Rates
- Frontward Rate
- Interest Rate Parity (IRP)
What Is Swap In Forex,
Source: https://corporatefinanceinstitute.com/resources/knowledge/trading-investing/foreign-currency-swap/
Posted by: reedcraver1962.blogspot.com


0 Response to "What Is Swap In Forex"
Post a Comment